
- 1800 327 253
- 58 Ashmore Rd, Bundall QLD 4217

A middle ear infection (also known as otitis media) is an infection of the middle ear. This is the air-filled space behind the eardrum that contains the tiny vibrating bones of the ear. Ear infections are very common and are usually painful, therefore ear infection treatment may include pain management and monitoring the symptoms.
Antibiotics often assist in clearing middle ear infections, however in some surgery may be required in some individuals with re-occurring infections.
Re-occurring infections without prompt management may cause hearing problems and other serious complications. Generally, this type of ear infection is more common in children than adults.
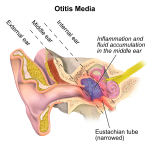
This condition may cause:
Diagnosis is made by examining the ear drum with a microscope, the ear drum may appear to be swollen and red.
Middle ear infections are usually caused by a viral or bacterial infection and often happen during or after a cold.
Mild cases can be treated quickly with paracetamol, however, some lead to the condition known as glue ear. This is when the fluid in the middle ear thickens to a glue-like consistency, therefore causing slight deafness. Treatment for glue ear may include nasal sprays to clear the eustachian tubes or antibiotics. If the issue isn’t resolved within six weeks, individuals may need a referral to an ENT experts for surgery for ventilation tubes.
Excessive ear wax can inhibit the ears from equalising, therefore causing more pressure and more pain. If you have excessive wax in your ear canal, having microsuction will help to release pressure build up.
A GP or audiologist can perform a tympanometry test to diagnose a middle ear infection.
Children aged six months or less will generally require an antibiotic, however older children may not need them.
If antibiotics are prescribed, it is important to finish the whole course of medication, even if symptoms improve after a few days because stopping treatment early promotes the growth of drug-resistant bacteria.
Your doctor may occasionally prescribe ear drops. Other medications, such as decongestants do not help middle ear infections.
Related Tag: Blocked Ear Wax Removal







Located in Bundall (formerly in Mermaid Beach), Ear Cleaning Clinic is the Gold Coast's only dedicated micro-suction ear wax removal clinic. We also stock a wide range of swim plugs, sleep plugs and ear care products. Hear Better. Feel Better.